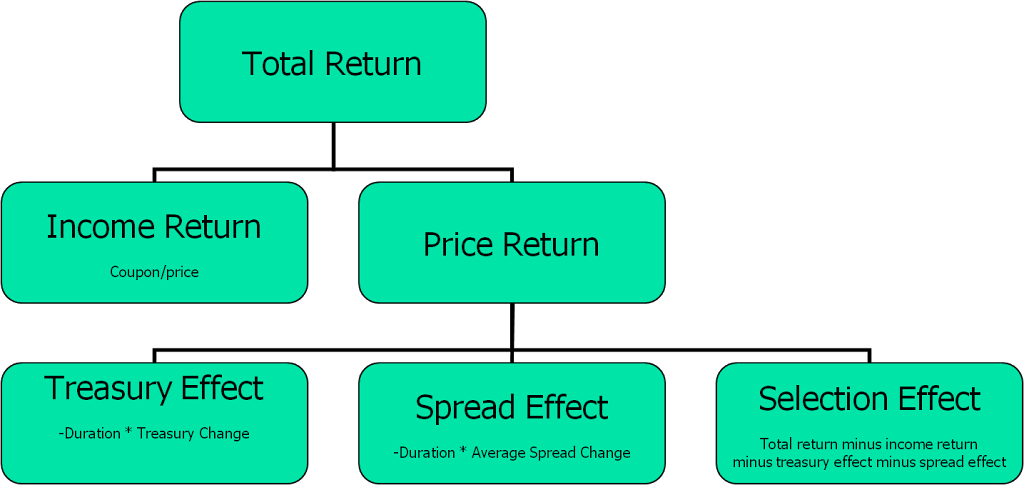
For many CIPM Expert Level candidates, fixed income attribution is the most difficult topic. This is evident when I teach TSG’s CIPM prep classes, as we devote an entire afternoon to the subject. Among the three models that candidates are required to learn is the Campisi model, which is based around the idea of decomposing bond performance according to the picture above.
Over the next few days, I will present various points on the Campisi model, in order to simplify it for candidates. This model is actually not very complicated – it is fairly intuitive – but candidates might benefit by having a roadmap to guide them through the process of calculating the attribution.
The diagram above is a decomposition of bond performance. Thus, it can represent the decomposition of a single bond, a group of bonds, a portfolio of bonds and/or a benchmark of bonds.
The first level of decomposition applies to any asset one may own in a portfolio. Return on an asset comes from two sources:
- income and expense (interest, dividends, and other expenses)
- price change (i.e., gains and losses, both realized and unrealized)
In our situation, of course, we are dealing with bonds, so the income is from interest.
The next level of decomposition, which breaks up the sources of price change, is specific to bond investments. Price change on bonds comes from three sources:
- price change that is due to changes in interest rates on the Treasury yield curve
- price change that is due to changes in spreads that non-Treasuries of a specific class (bond class and/or ratings class) pay above Treasuries of the same duration (average spreads)
- price change that is due to security specific traits of bonds that cause them to perform differently than the average for their class (nominal spreads)
A Treasury bill, note or bond could have return from the first and third sources.
A non-Treasury fixed income security could have return from all three sources.
Thus, the terminal nodes in the tree represent the lowest level of the decomposition:
- income
- price change due to changes in Treasury rates
- price change due to changes in the average spreads of a risky bond class
- price change due to security specific traits (i.e., due to nominal traits)
In order to calculate the Campisi attribution effects, the return of both the portfolio and the benchmark must be decomposed into contributions from these sources. Thus, in order to calculate the Campisi attribution effects, the following steps must be taken (i.e., your roadmap):
- Decompose the benchmark return into:
– income contribution
– Treasury contribution (i.e., price change due to changes in Treasury rates)
– spread contribution (i.e., price change due to changes in the average spreads of a risky bond class
- Decompose the index portfolio return into:
– income contribution
– Treasury contribution (i.e., price change due to changes in Treasury rates)
– spread contribution (i.e., price change due to changes in the average spreads of a risky bond class - Calculate the index portfolio spread change. This is the change in interest rates that will be used to calculate the spread contribution of the portfolio (more on this in a subsequent blog post).
- Decompose the portfolio return into:
– income contribution
– Treasury contribution (i.e., price change due to changes in Treasury rates)
– spread contribution (i.e., price change due to changes in the average spreads of a risky bond class
– security specific contribution - Calculate the attribution effects as the value added contributions:
– income effect = portfolio income contribution minus the benchmark income contribution
– Treasury effect = portfolio Treasury contribution minus the benchmark Treasury contribution
– spread effect = portfolio spread contribution minus the benchmark spread contribution
– selection effect = portfolio selection contribution (note – the benchmark has no selection contribution)
The picture below shows my scribblings from doing this in a recent class in the form of an attribution effects scoreboard – I recommend candidates mimic this during the exam to keep track of where they are:
More details to come!